What Are Pickles?
One of the oldest ways of food preservation is pickling. Pickling was the sole means to preserve certain foods for future use until the introduction of modern refrigeration. Pickling began as a way to preserve crops that were either unusual or seasonal, and whose availability was limited by nature and agriculture. Pickling may be traced back to India, where it is thought to have begun around 4,000 to 5,000 years ago. Food output declined during the summer due to scorching temperatures and a shortage of water. As a result, there was a need to preserve excess food produced throughout the winter, and pickling was devised to solve this problem. Sour cucumber pickles are the most frequent pickled vegetables, and they contain energy, protein, fat, carbs, dietary fiber, and sugars. Iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and sodium are among the minerals contained in this pickle. This pickle may also contain the B vitamins thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B-6, folate, and B-12, as well as vitamin C and all fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D, and K).
5 Popular Pickles Around the Globe
Pickles from India
Unripe fruits such as mangoes, Indian gooseberries, unripe tamarinds, and lemons have long been utilized in India. Other vegetables that are pickled include gherkin, bitter gourd, carrot, cauliflower, ginger, garlic, onion, jackfruit, and citron. Pickling is often done with just one vegetable or unripe fruit, however, a mixture of two or more vegetables or immature fruits is occasionally prepared. Pickles made from vegetables and unripe fruits are generally prepared with extreme caution so that they do not rot and can be stored all year. Non-vegetarian pickles such as chicken, fish, shrimp, and mutton, are also popular.
European Pickles
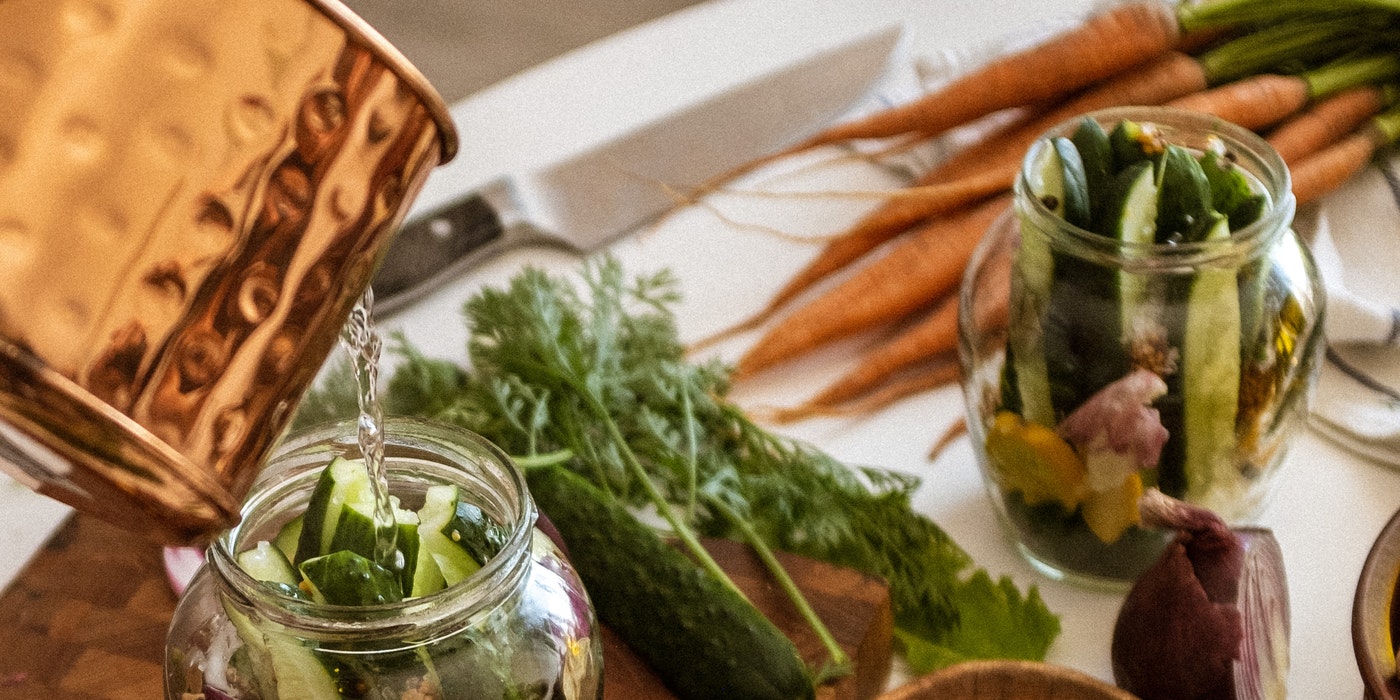 Pickles are commonly made in the United States, New Zealand, Switzerland, and many European countries from salted cucumbers, gherkins, and other vegetables soaked in vinegar. Fruits including peaches, pears, and apples, in addition to cucumbers and gherkins, are pickled. These pickles have a sweet, tart, and salty flavor profile, whereas Indian pickles have a pungent flavor profile. Fermented or crock cucumber pickles, fresh pack or quick process cucumber pickles, and refrigerator and freezer cucumber pickles are the most common types.
Pickles are commonly made in the United States, New Zealand, Switzerland, and many European countries from salted cucumbers, gherkins, and other vegetables soaked in vinegar. Fruits including peaches, pears, and apples, in addition to cucumbers and gherkins, are pickled. These pickles have a sweet, tart, and salty flavor profile, whereas Indian pickles have a pungent flavor profile. Fermented or crock cucumber pickles, fresh pack or quick process cucumber pickles, and refrigerator and freezer cucumber pickles are the most common types.
Pickles from Korea
Kimchi is a popular pickled product in Korea prepared from fermented spicy cabbage and a variety of vegetables such as soybeans, fish, oysters, and a variety of other ingredients. The Korean pickling method has Chinese origins, however, unlike traditional Chinese cabbage pickles, the Korean pickling technique has its own modifications based on local flavor and ingredients. In Korea, there are two types of pickling processes: one in which the components are fermented with fiery chili pastes, and the other in which milder variations are pickled in water.
Chinese Pickles
Pickles are highly popular in Asian nations such as China, where they have been prepared for thousands of years. Cabbage, lettuce, bitter melon, cucumber, carrot, and shallot are among the vegetables used in Chinese pickles. These and other veggies are tossed in vinegar with sugar and salt. Aside from vegetables, eggs (especially duck eggs) are preserved by combining salt, earth, hay, and other materials in a sealed container and allowing them to mature for about a month. In certain pickling procedures, soy sauce is used instead of vinegar for fermentation, and seasonings like ginger, garlic, chile, or peppercorns are added for a spicy, distinct flavor.
Fresh Pickles
Chutneys, either instant or fresh pickles, are also made. These instant chutneys are only meant to last a few days. When it comes to making instant pickles, you have a lot of options. Chutneys are made with a variety of vegetables, herbs, and seasonings.
4 Benefits of Pickles
There are numerous pickles available that are high in nutrients and can benefit our bodies in a variety of ways. Let’s take a closer look at the advantages.
Probiotic Benefits
As previously said, (most) pickles are fermented foods, which means they’re strong in probiotics and beneficial to your digestive system. The carbohydrates in the vegetable are broken down and converted into lactic acid during the fermentation process, which provides probiotic advantages. You probably already know that a happy gut equals a happy life: the microbiome regulates not only digestion but also your immune system and even helps you maintain a healthy weight.
Restoring Electrolyte Balance
Electrolytes are salts that the body requires to function properly. When a person becomes dehydrated, they may lose electrolytes as well. Pickles are heavy in sodium, which means they’re high in electrolytes as well. This shows that pickle juice could be used to help persons who have a fever, are vomiting, or are dehydrated rehydrate their electrolytes. Pickle juice is used by some athletes to replenish electrolytes after an exercise. There is no evidence that pickle juice is a better option than water or electrolyte drinks in terms of hydration. A modest bit of pickle juice, on the other hand, may be a nice option for someone who enjoys it.
Rich Source of Antioxidants
Pickles have a lot of antioxidants in them. The antioxidants included in the veggies or unripe fruits are maintained since they are stored fresh without being cooked. Antioxidants are micronutrients that may aid in the protection of our bodies against free radical attacks. By eating foods strong in antioxidants, we may be able to defend ourselves from these radical attacks.
Provides Essential Vitamins and Nutrients
Leafy vegetables or herbs such as coriander, curry leaves, spinach, parsley, and amaranth are used to make fresh pickles, dips, or chutneys. Fermented veggies and herbs, such as kimchi, are a fascinating and attractive approach to entice kids to eat more leafy vegetables and herbs that might otherwise be dull to them. Eating a freshly produced pickle may provide critical vitamins like vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin K, folate, and minerals like iron, calcium, and potassium, as well as taste. Vitamins and minerals are essential micronutrients that can help us avoid diseases, develop immunity, strengthen bones, improve vision, and treat a variety of other conditions.
Side Effects of Pickles
Although pickles have their benefits, there are some disadvantages that come with them:
High in Sodium
 Pickles are helpful for athletes whose electrolytes have been depleted, but because they’re fermented with salt, they carry a lot of sodium, averaging 313 milligrams per serving.
Pickles are helpful for athletes whose electrolytes have been depleted, but because they’re fermented with salt, they carry a lot of sodium, averaging 313 milligrams per serving.
Excess Preservative with Little Probiotic Benefits
The secret to reaping the nutritious benefits of pickles is to purchase them chilled. Most store-bought pickles are prepared with vinegar, which eliminates the majority of their gut-healthy advantages. Preservatives and extra sodium are frequently added to processed pickles in order to extend their shelf life. Refrigerated ones, on the other hand, provide all of the health benefits.
Now that you Know…
While processed, jarred pickles that have been sitting on store shelves for months aren’t exactly superfoods, fresh pickles are. Also, note that almost all pickles have a high salt content. It not only enhances the flavor of the pickle, but it also functions as an anti-microbial agent, keeping bacteria, yeast, and fungi at bay. Pickle consumption, on the other hand, can generate its own set of difficulties. One of the most serious side effects of consuming too much salt is hypertension. It is known to be one of the leading causes of strokes and heart attacks, particularly in the elderly. In addition, as people become older, their blood pressure rises.